how do they test for testicular torsion|testicle torsion prognosis : exporter Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical . Resultado da Did you know that the Ruby is the Birthstone for July? What makes the ruby so coveted? Did you know it’s almost as hard as a diamond? Learn more .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Nas suas principais ruas, se mistura o clima carnavalesco e .
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding.
Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, . Introduction. Scrotal complaints are relatively common in the emergency department, comprising at least 0.5% of all emergency department visits. Testicular torsion . A history and physical exam consistent with testicular torsion mandates an immediate surgical consult for scrotal exploration. If history and physical exam suggest .
Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical .
Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord.Individual clinical findings that best predict testicular torsion include nausea and vomiting, past trauma, a tender testicle, an abnormal testicular lie (i.e., elevated or transverse), and.Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys .
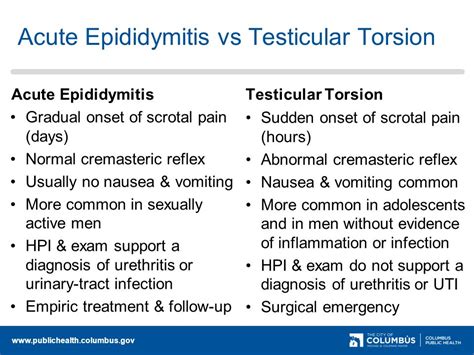
Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages 12 to 18 or babies. Without blood supply, the tissue of your testicle can die in a few hours . See a doctor right away if you think you have . Testicular torsion, or twisted testicle, can be extremely painful. . Many health experts call torsions “winter syndrome” because they commonly occur during cold weather. For example, a .
No special preparation is necessary to do a testicular self-exam. You might find a testicular self-exam is easier during or after a warm bath or shower. Heat relaxes the scrotum, making it easier for you to check for anything unusual. What you can expect. To do a testicular self-exam, stand unclothed in front of a mirror. Then: Look for swelling.
Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies. Testicular torsion is a very serious condition and is considered a medical emergency. Rotation of the testicle around the spermatic cord can cause obstruction of the arterial blood flow to the testicle, as well as the venous blood outflow, which can ultimately lead to necrosis or death of the testicular tissue. How common is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion occurs in teenage boys aged 13-18 years. This is found to happen in around 1 in 4,000 young men. Newborn babies and younger children sometimes develop this problem. It is uncommon over the age of 25 but does occur sometimes in older adults and can occur at any age.Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become .
What is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion happens when one of your testicles twists around. Each testicle is attached to a spermatic cord, which contains blood vessels that carry blood to the testicle. In testicular torsion, this becomes twisted (called torsion) and blocks the flow of blood to the testicle. Testicular torsion is an emergency.
testicular torsion vs epididymitis signs
Testicular torsion in young boys and teen boys occurs when the testicles are not completely attached in the scrotum. This lets the testicles move more freely and twist. . He may also have tests, such as an ultrasound. This is a painless imaging test that uses sound waves to see the scrotum and testicles and check blood flow.
Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. . Masses both outside and within the testicles may be benign or malignant and should be evaluated as soon as they are detected. top of page . the twisting of the spermatic cord that contains the vessels that supply blood to the . A testicular ultrasound is a diagnostic test that obtains images of the testicles and the surrounding tissues in the scrotum. It’s also known as a testicular sonogram or scrotal ultrasound. Prehn's sign is a clinical finding that helps clinicians determine whether testicular pain is caused by epididymitis or testicular torsion. A positive Prehn's sign, characterized by pain relief from the maneuver, is indicative of epididymitis, or the inflammation of the epididymis (i.e., duct running behind the testes).
Testicular torsion requires immediate medical attention. It can happen to boys and men of any age, but most often occurs in boys aged between the ages of 12 and 18. . Because the testicles hang from this cord, it's possible they can twist around inside the scrotum and cut off their own blood supply. This is called testicular torsion.
Testicular torsion can be extremely painful and is an emergency situation. It happens when the testical cord that carries blood to the testicles twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicles. . Sometimes, they do not attach properly or entirely. The spermatic cord—which connects the testicles to the abdomen—may then twist onto .If a healthcare provider finds a lump during a testicular exam, they may: Shine a light through the back of your testicle (transillumination). Transillumination helps the provider see the location of the lump and its size. . They’ll conduct a physical exam, order tests and recommend treatment, if necessary, according to the type of lump you . Investigations. The diagnosis of testicular torsion is a clinical one, therefore any suspected cases should be taken straight to theatre for scrotal exploration.. However, in cases with sufficient equipoise, Doppler ultrasound . Testicular Torsion, while rare, causes testicles to twist, lose blood flow and die. . they found—prepare to reflexively clamp your legs shut at this next bit—the testicle was so squeezed, it .
Urine and blood tests. Samples of your urine and blood may be sent to the lab for testing, too. Ultrasound. This imaging test uses sound waves to create pictures of your testicles. The test can show if you have testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a twisting of the testicle that can cut off blood flow. Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the ideal imaging modality to evaluate the scrotal contents. . Ultrasound is not a perfect test for testicular torsion, especially in the very young. For example, 40% . Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity. The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis. .
Testicular torsion can occur at any time – e.g. while sleeping, sitting on the couch, or after activity and trauma. Rapid growth of the testicles during puberty is also a risk factor. Who is at risk of testicular torsion? Most cases are between the ages of 12 and 18, but testicular torsion can occur at any age. Signs and symptomsThe cause of testicular torsion is unknown, but it may arise if the testicle or the protective sac around the testicle is not completely attached to the scrotum, allowing it to move around freely. Often times, this is the result of a congenital defect. The condition may also be inherited or occur after injury to the scrotum or testicle.American Urological Association Curriculum on Acute Scrotum: This case-study offering from the association's medical school curriculum covers the differential diagnosis of acute scrotum with a concentration on 6 conditions: epididymitis, hernia, scrotal trauma, testicular torsion, testicular tumor, and torsion of testicular appendices.A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes).
Testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a painful condition in which your testicular blood supply (the spermatic cord) twists and cuts off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion affects about 1 in 4,000 people under the age of 25. At what age should an orchiopexy be done? Among these, testicular torsion is the most important and time-sensitive diagnosis to make. Delay in seeking medical care or delay in diagnosis for these patients can result in significant morbidity, including infertility. 2. The use of point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) for the evaluation of patients with acute scrotal pain can be a very .Anatomy of the normal testis, bell clapper anomaly and intravaginal testicular torsion. Blue testis, Green epididymis, Lavender spermatic cord and vessels, Red tunica vaginalis. Normally, the epididymis extends along the full length of the testis posterolaterally so that the upper and lower poles of the testis are covered and the tunica vaginalis parietal lamina is anchored to the .
testicular torsion survival rate
Triples.com.ve triples.bet Tu agencia de loteria On Line, jueg.
how do they test for testicular torsion|testicle torsion prognosis